By Muhammed Hassan
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Nigeria alone accounts for more than 100,000 new sickle cell births every year1. Statistics from African region of the World Health Organization (WHO) puts the prevalence of the Sickle cell trait in Nigeria at 20% to 30%2. In sub-Saharan Africa, very few control programs exist and those that do exist, lack national coverage or the facilities to manage patients. Proactive, routine screening for sickle cell disease is not common practice so diagnosis is usually made when a severe complication occurs.
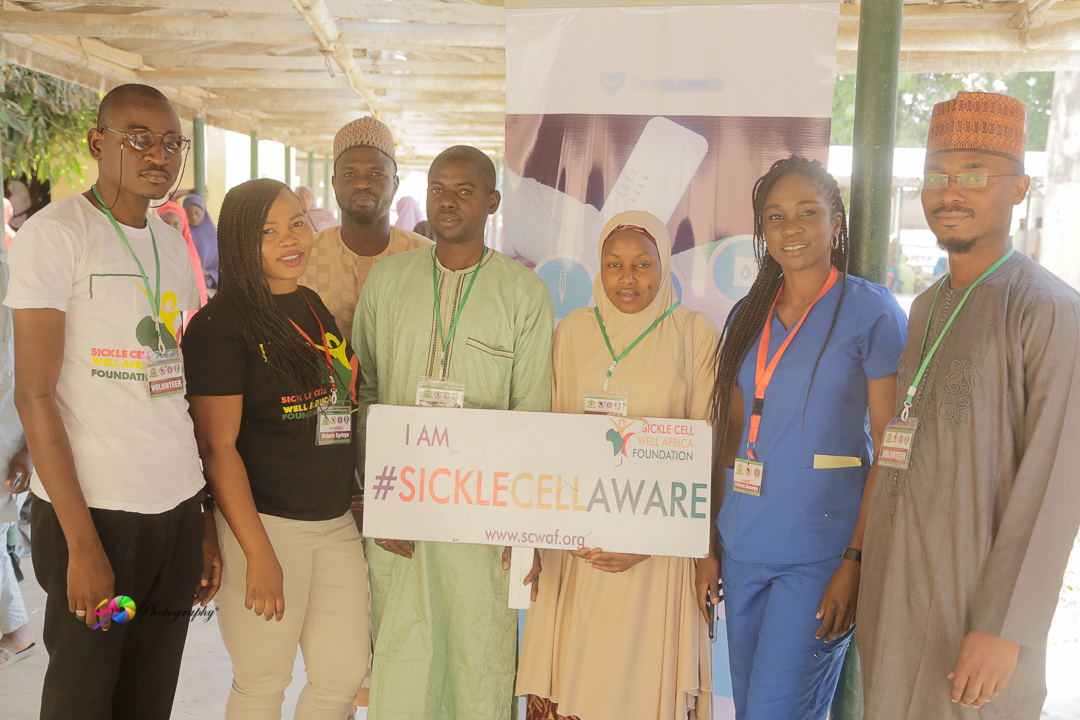
At eHealth Africa, we aim to improve the quality and availability of healthcare for underserved populations and to increase access to timely and quality diagnostic services. We partnered with Sickle Cell Well Africa Foundation (SCWAF), Pro-Health International and the Presidential Committee on the North- East Initiative (PCNI) to hold a two-week outreach in Bajoga LGA, Gombe state, and Toro LGA in Bauchi State from the 2nd-16th December 2018.
The team hosted community and school outreaches in both LGAs. Beneficiaries of the outreaches in both LGAs were educated about Sickle Cell Disease (SCD), inheritance, signs and symptoms, and the importance of genotype testing for SCD and prevention. Free genotype tests were conducted using the Sickle Scan Rapid Test Kit.
Patients who tested positive for SCD and those who presented with severe complications were given routine medication, advised on first-level crisis management and referred to tertiary hospitals. eHealth Africa captured, stored and analyzed the results of the tests. The analyses provided insight into the geographic distribution of patient and the average age distribution of patients who tested positive for SCD and the categories of complications presented at the outreach.
eHealth Africa, Pro-Health and SCWAF presented these results at stakeholder meetings in both states and provided evidence-based recommendations to enable the states to tackle Sickle Cell Disease. Going forward, eHA intends to work with Pro-Health to develop a comprehensive data collection tool which will support tracking and follow up of SCD patients in Prohealth Sickle Cell Clinics.
The Impact: