By Daniel Ojabo
A vast number of the most vulnerable human settlements in Africa have remained unmapped. In the case of a public health emergency, knowing where people live, the best ways to get in and out, and the locations of basic necessities such as hospitals are of paramount importance.
The paucity of accurate geospatial data, including population settlement data, presents a major obstacle to adequate decision-making across Nigeria and remains a barrier to development. The Nigeria GRID (Geospatial Reference Information Database) project is part of a bigger global initiative; a multi-country, multi-donor initiative that aims to collect and store geospatial data across several African countries.
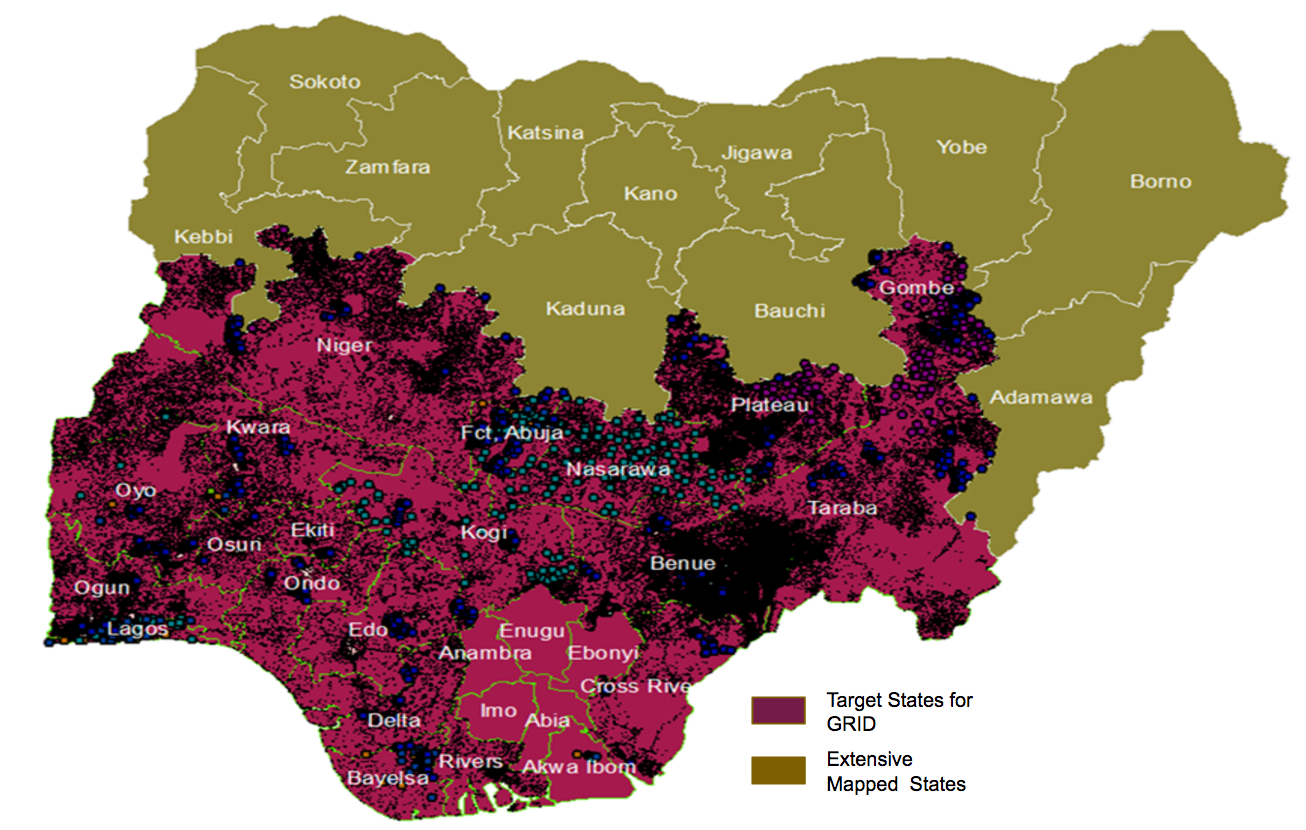
Through the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) in Nigeria, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) via eHealth Africa (eHA) has mapped 11 out of 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) of Nigeria. Through the GPEI, eHA deployed a combination of remote sensing satellite imagery, primary data collection, and geographic information systems to map over 140,000 settlements and other relevant points of Interests (POIs). The GRID project is now scaling up to the whole country and will complete the mapping of the remaining 25 states plus the FCT, collecting settlement names, geographic coordinates, and POIs such as health facilities, schools, and markets across the country.
Several attempts have been made to provide reliable geospatial data to the country. But despite this, there still exist significant gaps to be addressed regarding the quality, completeness, and sustainability of geospatial data available across Nigeria. In addition, there is a lack of capacity within the state and the federal government to leverage existing infrastructure to develop robust systems which can collate, manage, and enhance existing geospatial data. The capacity to develop innovative tools to effectively exploit geospatial data which can support improved decisions, policies and socio-economic resilience is also limited.
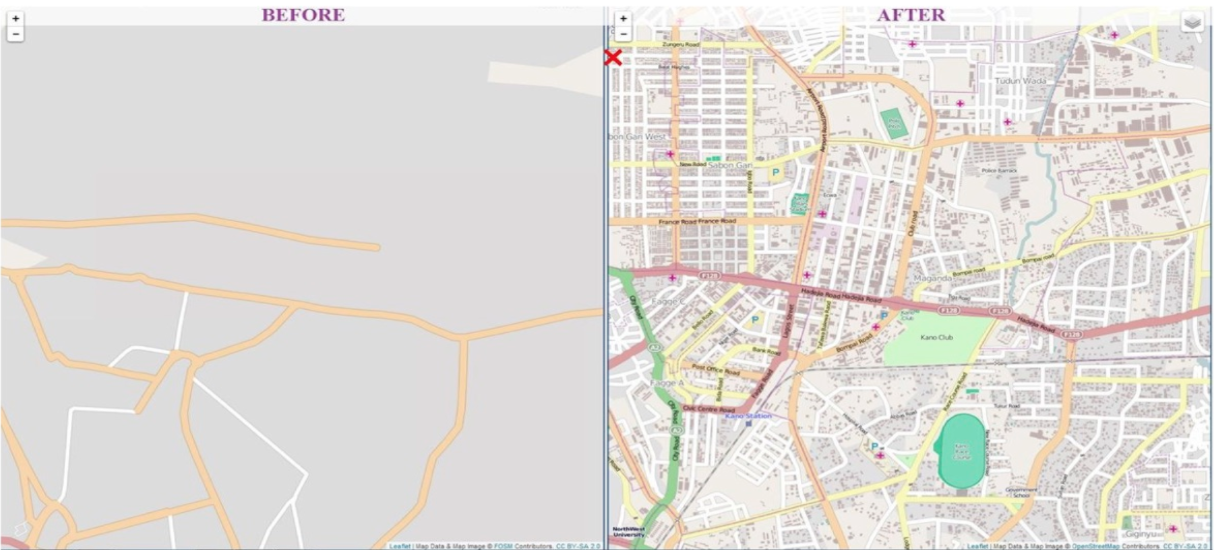
The GRID project aims to bridge this gap, by supporting state and federal government agencies to strengthen geospatial data availability across Nigeria. To do this, the project will adopt the same methodology used during the GPEI to map and provide geospatial data for the rest of the country. Over a period of 9 months, the GRID project will develop a geodatabase of settlements with GIS coordinates, population estimates, and other relevant POIs across 25 states and the FCT. The project will also build the capacity of the Nigerian government to utilize the data effectively.
eHA remains committed to the development of people-centric and data-driven technology solutions that connect and deliver better public health services for vulnerable communities in Africa. See more stories and articles about eHA's innovative work by signing up for our monthly newsletter.






