By Adaeze Obiako
“If you talk to a man in a language he understands, that goes to his head. If you talk to him in his language, that goes to his heart.”
This year, the United Nations is celebrating “International Translation Day” for the first time. The celebration is an opportunity to pay tribute to language professionals, whose work plays an important role in bringing nations together, facilitating dialogue, fostering understanding and cooperation, and contributing to the development and strengthening of world peace and security.
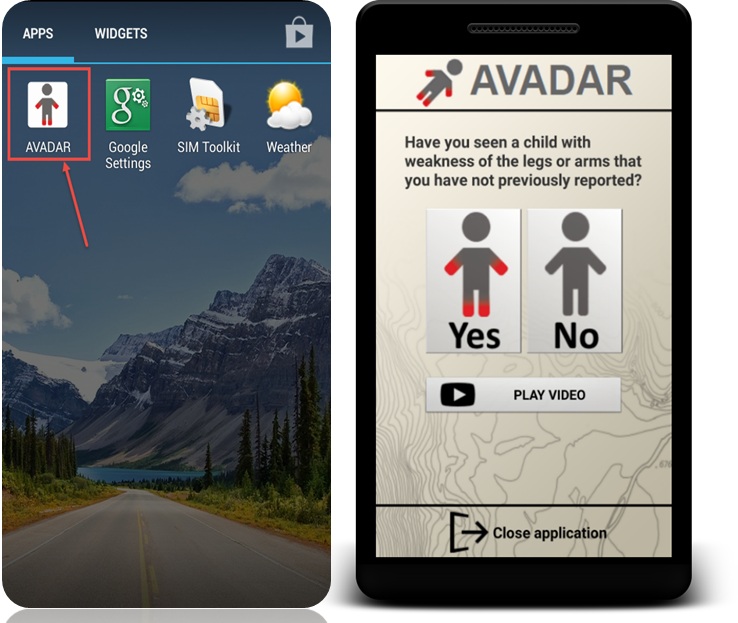
For eHealth Africa (eHA), translation has been instrumental to the success of several projects, particularly the Auto-Visual AFP Detection and Reporting (AVADAR) project.
When AVADAR commenced in 2016, we knew it was a worthwhile intervention towards the eradication of polio in Nigeria; however, we could not have anticipated just how much of a positive impact it would end up having on the Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) surveillance system across Africa. Between 2016 and 2018, AVADAR grew from a small pilot in two states in Nigeria to a full-fledged project across 8 West and Central African nations. Several factors contributed to the success and scale of the project, one of which was the educational AFP video embedded in the AVADAR mobile app used to train community informants on proper detection (and subsequent reporting to health authorities) of AFP cases within their communities.
This is where language came in.
The project management team, made up of the World Health Organization (WHO), country Ministries of Health, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Novel-T, and eHA, knew early on that the key to ensuring accurate AFP detection and proper use of the AVADAR app for case reporting lay with developing a sense of connectedness and trust between all stakeholders (from project implementers to health workers to community informants) through the breakdown of language barriers.
Part of the pre-implementation phase in each country included research into what languages were spoken by indigenes using the AVADAR app and the AFP video, and the entire app was translated into each applicable language. Below is an example of the AFP video translated into Hausa, a local language commonly spoken in northern Nigeria, Niger, Chad, Cameroon and the Central African Republic.
In addition to the AFP video and app being translated into multiple languages, the training facilitators (who train informants on how to use the app) and field officers (who provide weekly phone troubleshooting support to informants) were all indigenes of the implementing regions and fluent in the local languages to ensure ease of communication and understanding for the AVADAR informants.
As AVADAR continues operation across Africa, it is clear that we have the power of translation to thank for bridging the gap and allowing thousands of community members and health workers across different African nations to support the fight against polio. At this rate, it won't be too long before polio, like smallpox, is considered a public health issue of the "past".