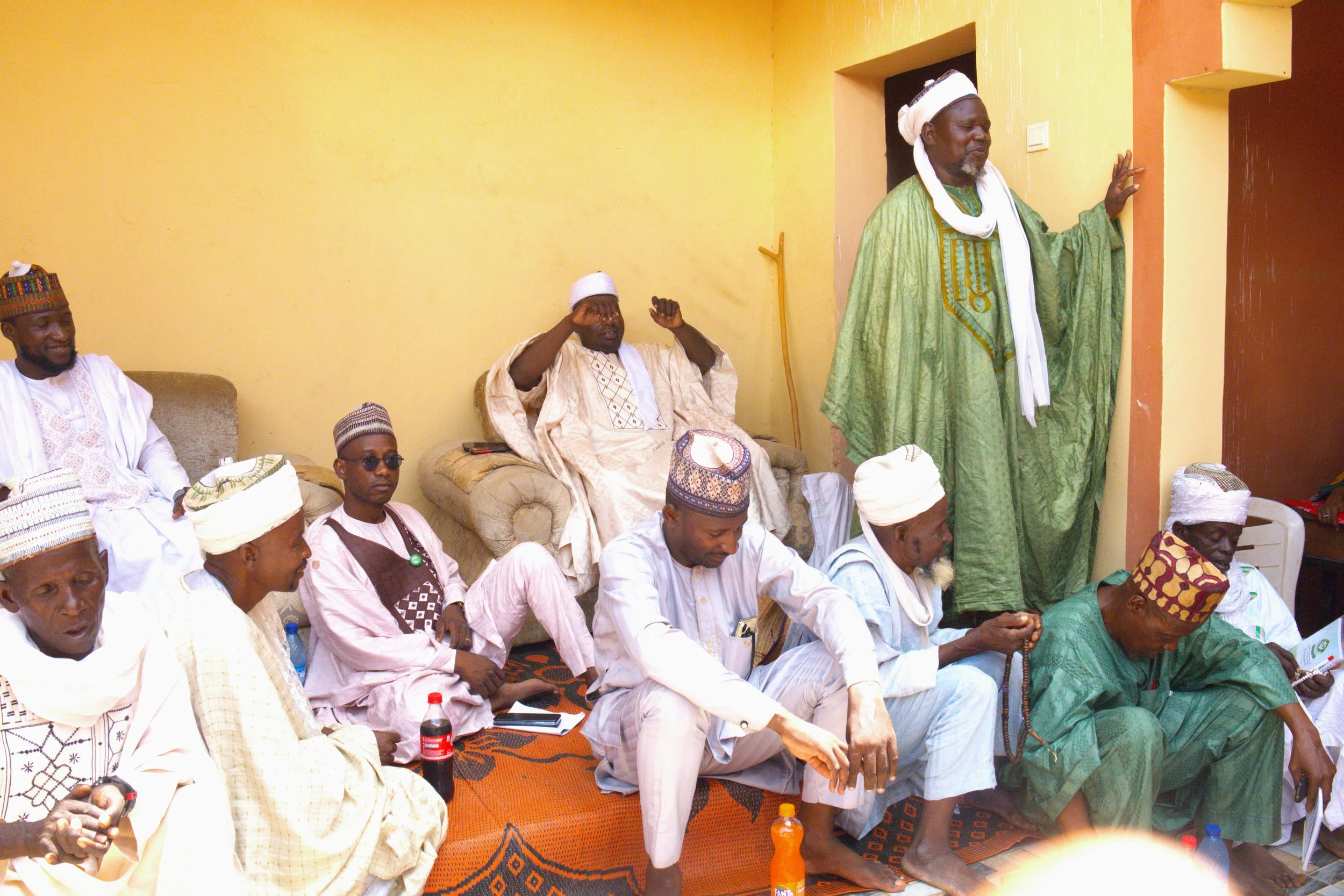
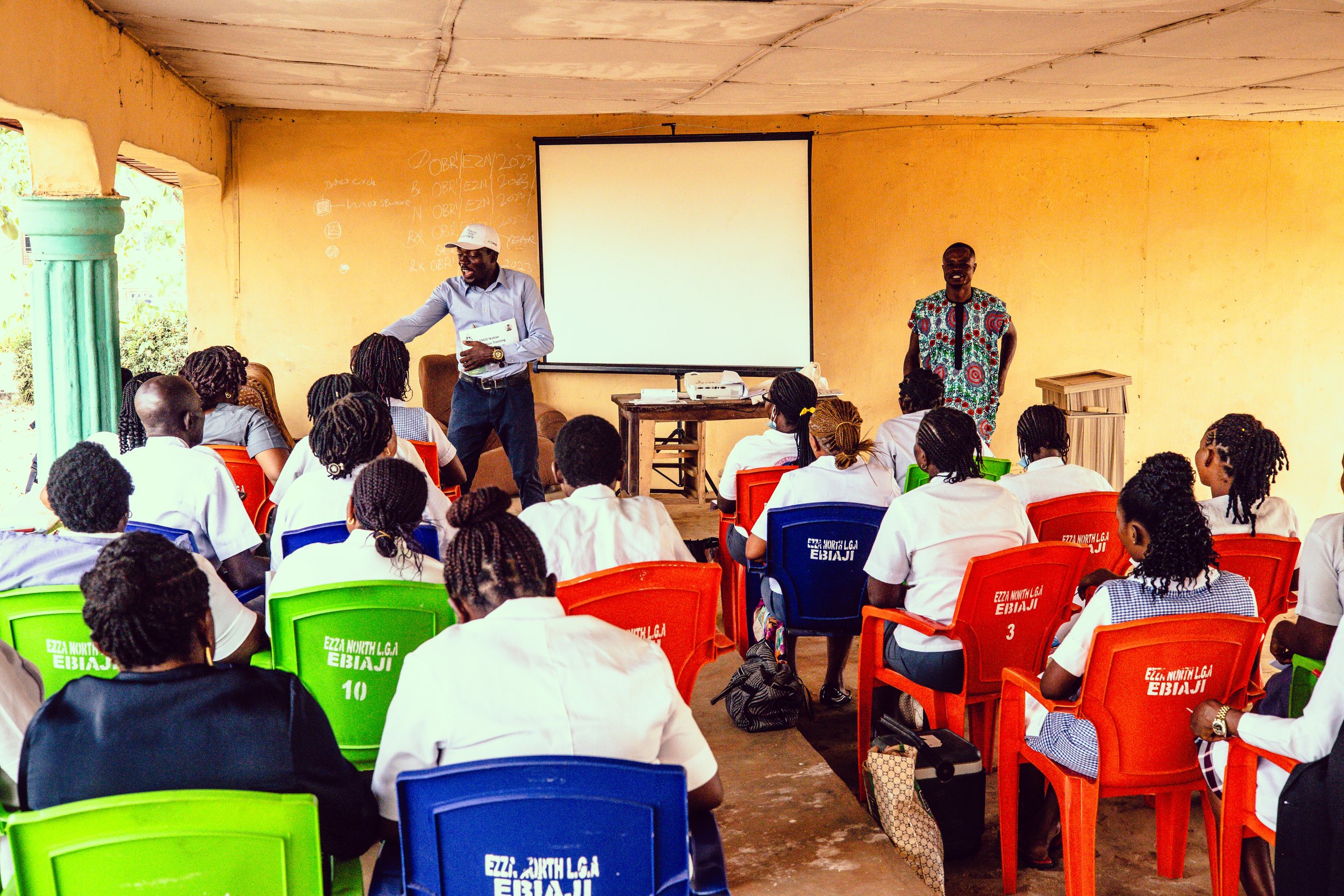
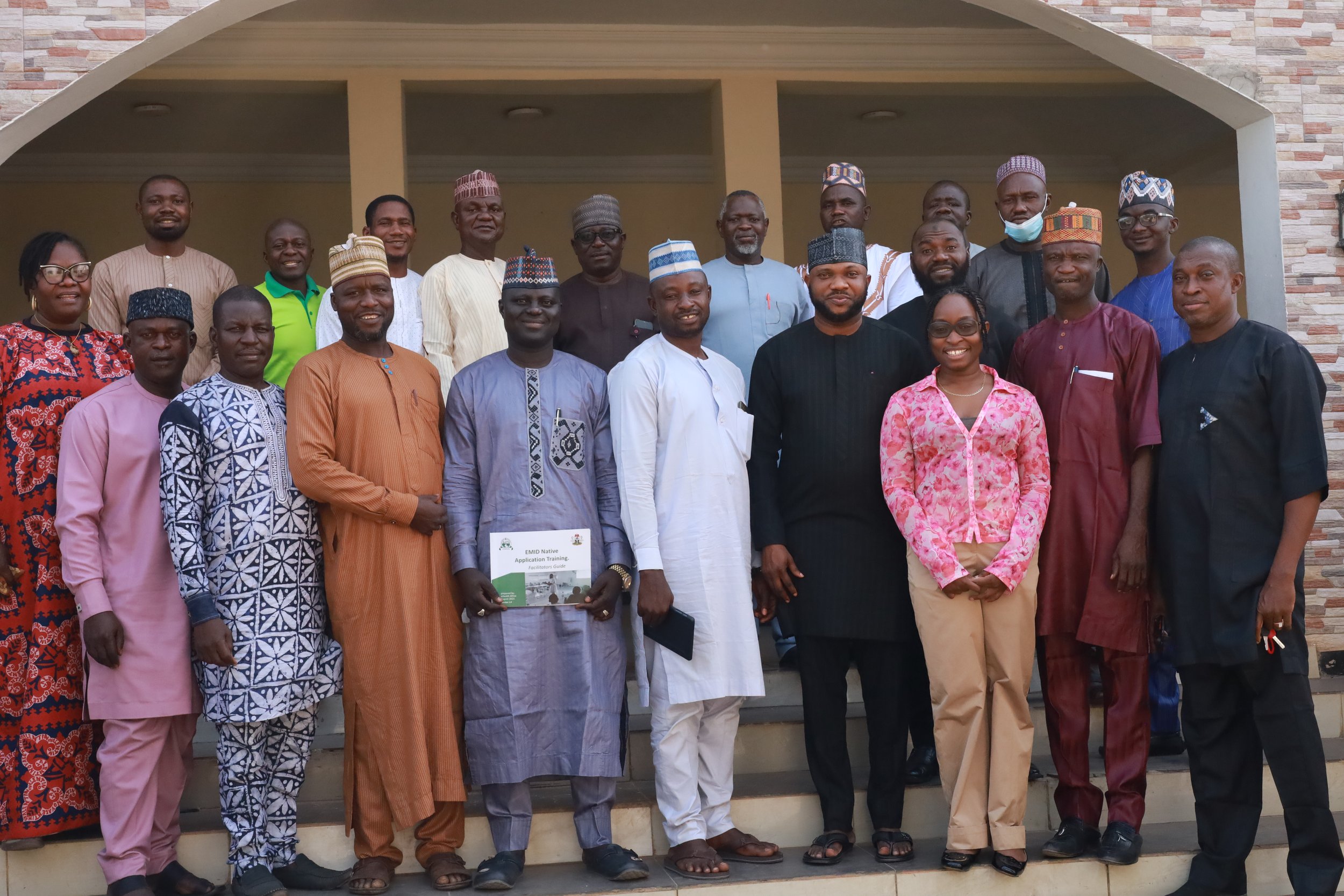
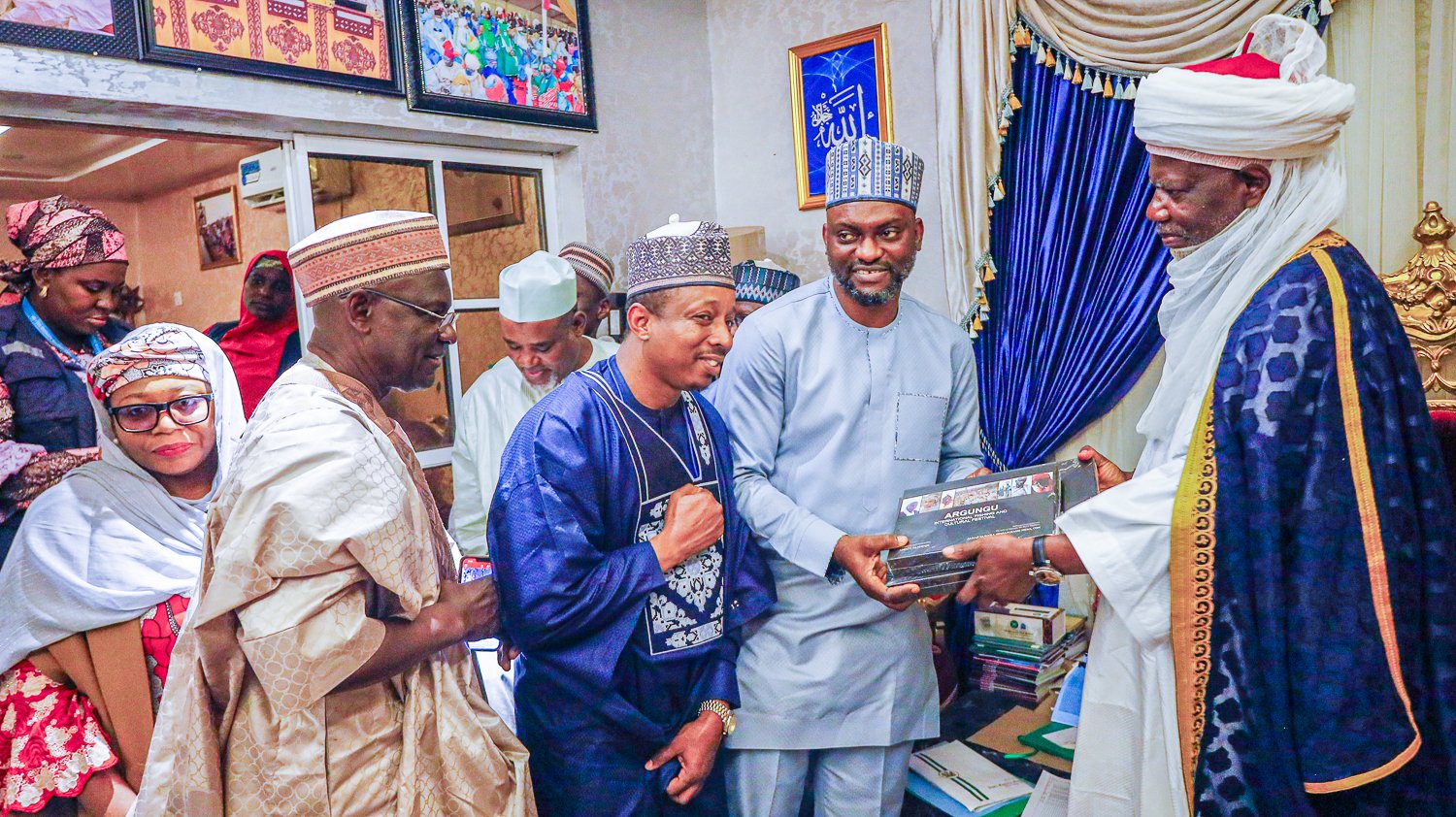
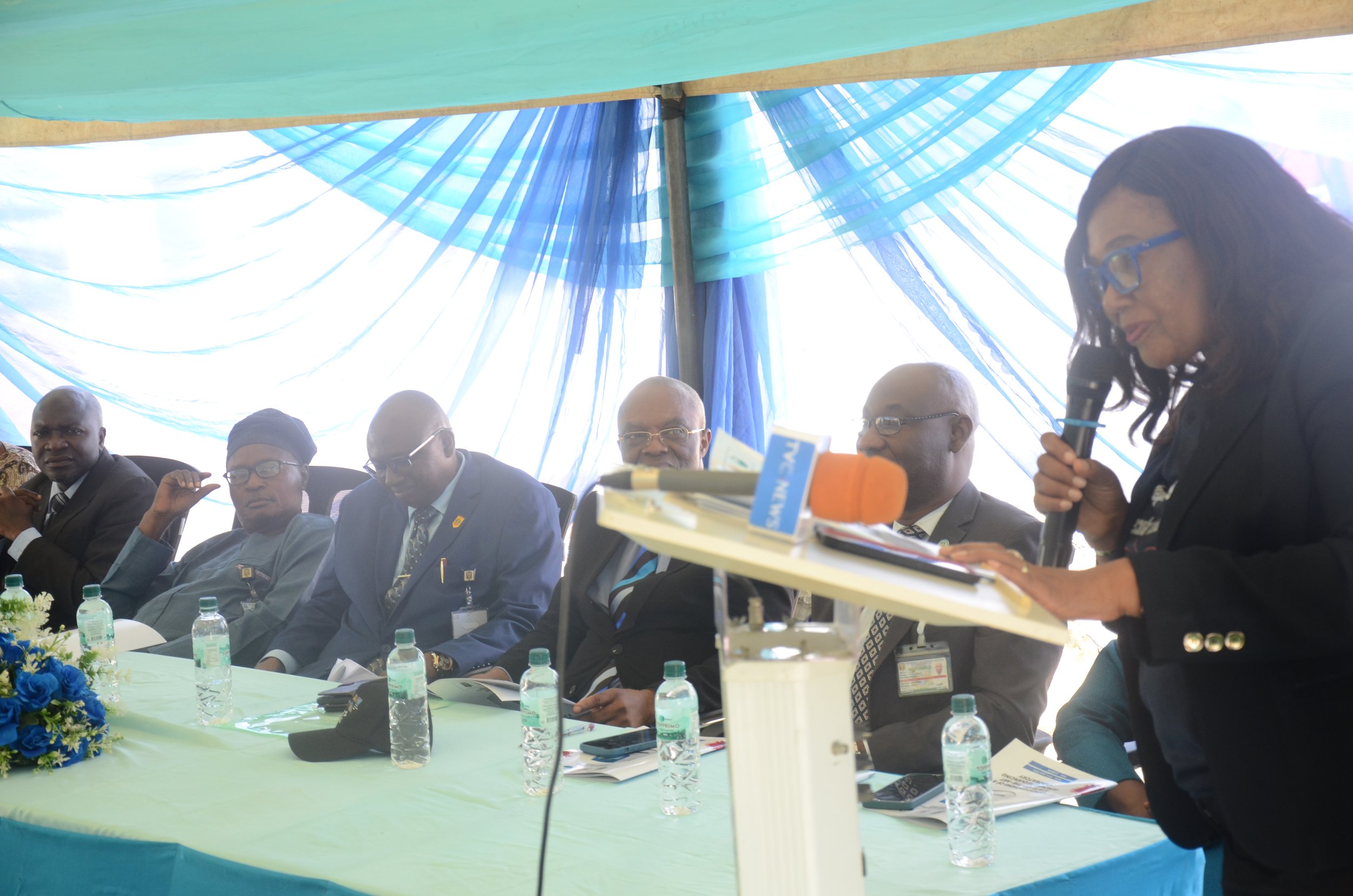
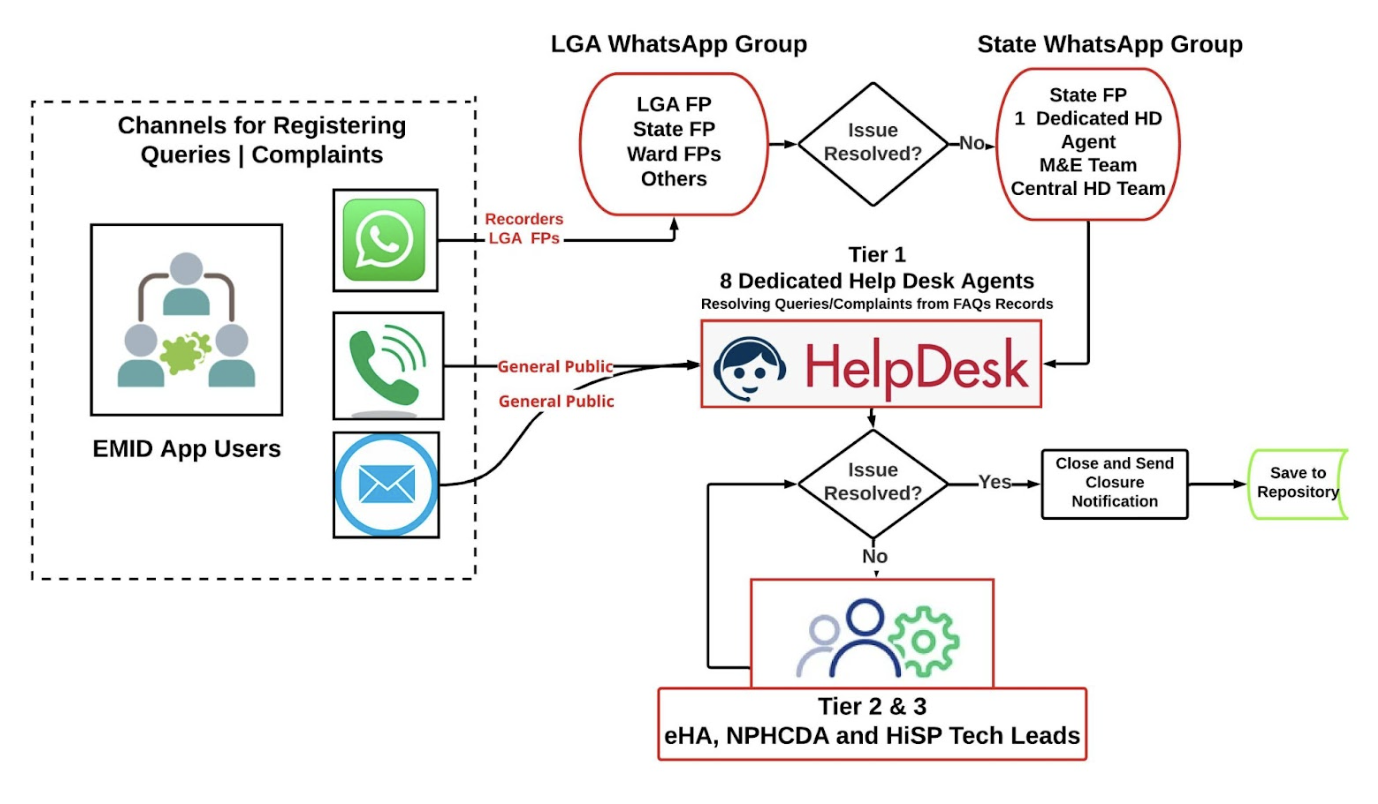
eHealth Africa representatives addressing Traditional Leaders in Wammako LGA of Sokoto state
by Moshood Isah
A visit to Sokoto State, Nigeria’s historical Caliphate, is always an intriguing experience, despite the often challenging weather. The city's rich history complements the profound respect held for its traditional and religious institutions, which are similarly revered across Northern Nigeria. These esteemed leaders have consistently played pivotal roles in public health initiatives.
According to the World Health Organisation, the strategic partnership with traditional leaders in Northern Nigeria since 2009 has been instrumental in eradicating the wild poliovirus in the country. Professor Oyewale Tomori, Chairman of the Expert Review Committee on Polio Eradication, emphasized that overlooking these influential community figures would have been a colossal error.
A cross-section of traditional leaders during a one-day engagement of frontline traditional leaders on Polio vaccination in Sokoto state.
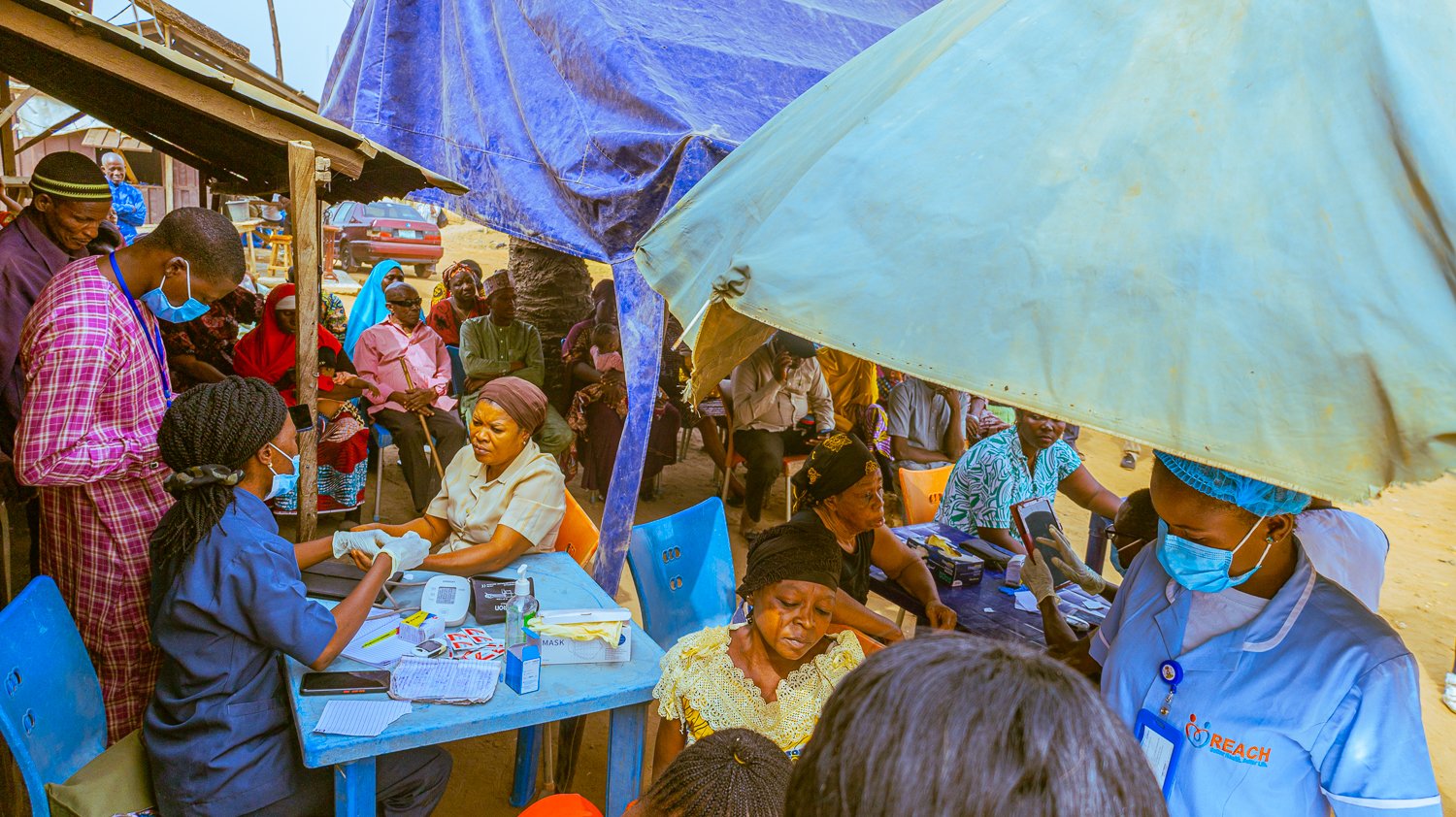
While these institutions were crucial in eliminating wild poliovirus in 2020, the emergence of the Circulating Variant Poliovirus demands a redoubled effort. To combat this new threat, traditional institutions across Northern Nigeria are being strategically deployed. Supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF), eHealth Africa is collaborating with the Sultan Foundation for Peace and Development and other partners to engage these leaders in polio campaign activities.
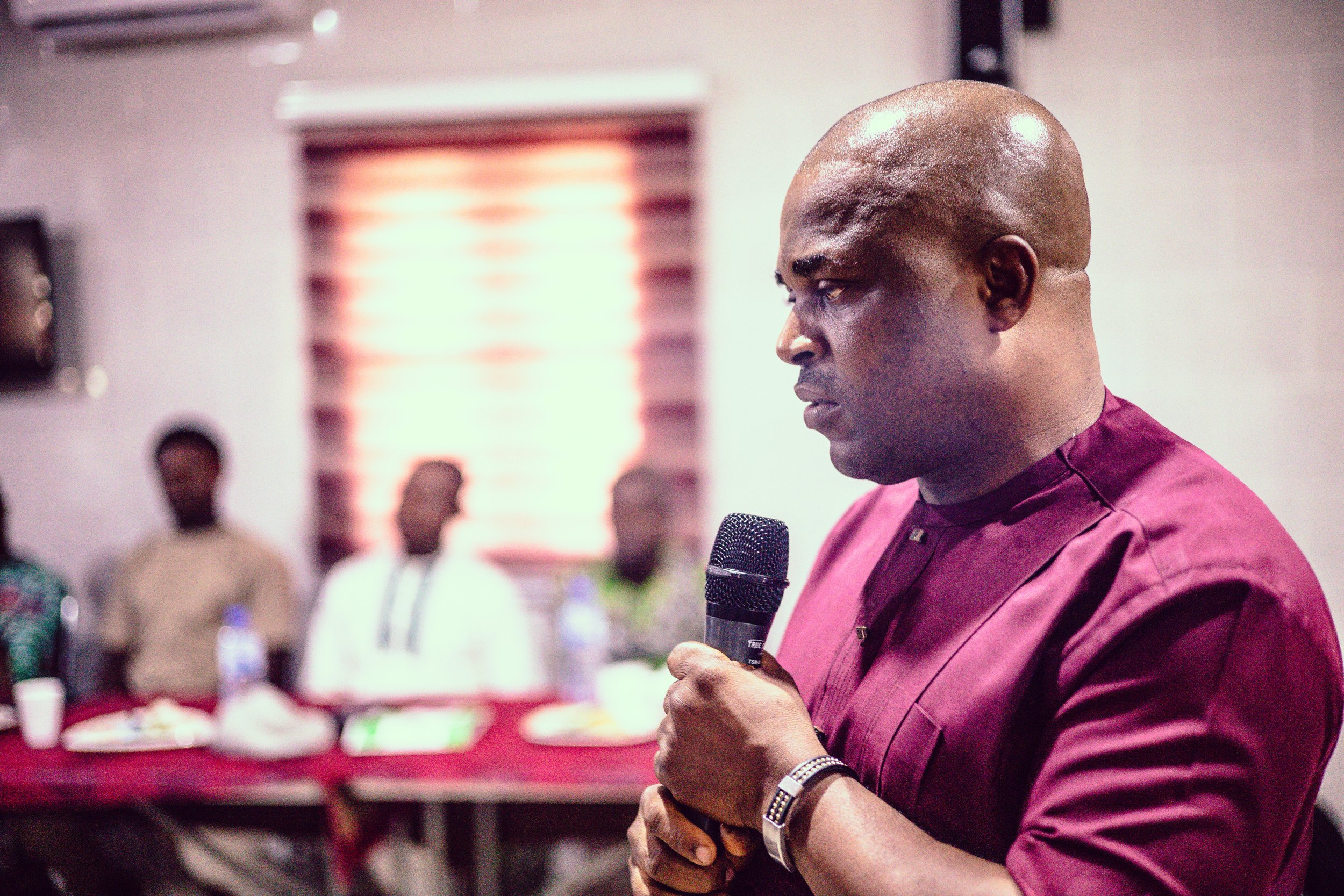
Haruna Yusuf Aliyu, Senior Program Officer at the Sultan Foundation for Peace and Development, highlighted the significant role of traditional leaders in a sensitization workshop held in Wammako Local Government Area. He revealed that many are spearheading vaccination campaigns directly from their palaces, which has significantly reduced vaccine hesitancy and boosted uptake.
“You can see traditional leaders going house to house, supervising vaccination teams and resolving cases of non-compliance while providing guidance to the teams to make sure that all households are actually identified, enumerated, then eligible children in those houses are vaccinated”, he said.
Through ongoing sensitization workshops, traditional leaders are equipped with the knowledge and tools to effectively communicate the importance of vaccination to their communities. Despite security challenges in some areas, Yusuf emphasized the organization’s commitment to working closely with community groups and traditional leaders to reach all children with essential vaccines.
Fatimah Howeidy, eHealth Africa’s Project Manager, expressed pride in supporting the Sultan Foundation and other partners to reduce vaccine hesitancy through the involvement of traditional leaders. The initiative has successfully bridged knowledge gaps and dispelled myths surrounding polio vaccination, particularly in underserved communities.
“It's so inspiring seeing traditional leaders in Sokoto state turn out in their numbers to participate in the polio campaign activities” she said. We are indeed excited that this intervention remains a platform to remind traditional leaders of the need to intensify the campaign to eradicate the Circulating Variant Poliovirus (cVPV2)”, she said.
The Engagement of Traditional Institutions (ETI) project aims to strengthen advocacy by traditional leaders, increase community ownership of polio eradication efforts, and reduce vaccine hesitancy in high-risk Northern states. There are plans to expand the initiative to Southern Nigeria.